India Cuts Fossil Electricity: A Historic Shift Toward Clean Energy
Introduction: A Personal Reflection on Energy and Our Future
Imagine waking up to the sound of birds chirping instead of the distant hum of coal-powered plants. Imagine a world where your children breathe cleaner air and where the electricity that powers your home comes not from burning fossil fuels, but from the sun, the wind, and rivers. This is not just a dream—it is increasingly becoming a reality in India.
In 2025, India made headlines by cutting fossil electricity output while reaching a new peak in clean energy generation. This milestone is more than just a number—it reflects the country’s commitment to sustainability, energy security, and a healthier future.
Table of Contents
Why India’s Shift from Fossil Electricity Matters
Environmental Impact
- Reduces carbon emissions, fighting climate change.
- Cleaner air in industrial cities, improving public health.
- Supports sustainable water and soil management.
Economic Significance
- Decreases dependence on costly fossil fuel imports.
- Strengthens energy independence through domestic renewable investment.
- Creates jobs in solar, wind, hydro, and nuclear sectors.
Social Benefits
- Improves public health and lowers healthcare costs.
- Reliable electricity supports education, digital growth, and industry.
- Reduces energy poverty in rural areas.
Record Clean Energy Generation in India
Solar Power Leading the Charge
- Solar electricity grew 25% YoY, reaching 85 TWh.
- India is emerging as a global leader in solar panel manufacturing.
- States like Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Tamil Nadu lead large-scale solar projects.

Wind Power Surges
- Wind energy rose 29%, totaling 47.2 TWh.
- Coastal regions with high wind potential became the backbone of India’s wind generation.
- Government incentives have encouraged private investment in wind energy.

Hydro and Nuclear Contributions
- Hydropower grew 14%, reaching 120 TWh.
- Nuclear energy hit a record 29 TWh, ensuring grid stability.
- Diverse energy sources help manage intermittent solar and wind generation.

Fossil Electricity Decline — A Turning Point
Coal Dependency Weakens
- Coal-fired output fell 3% to 675 TWh.
- Advanced coal technologies like ultra-supercritical plants are still used.
- Declining share signals India’s energy transition progress.
Gas Power Collapse
- Natural gas electricity generation dropped 34% to 13.75 TWh.
- High global prices and supply volatility reduced gas use.
- Highlights need for renewable backup systems for energy security.
India’s Energy Mix Transformation
Comparing Clean vs. Fossil Generation
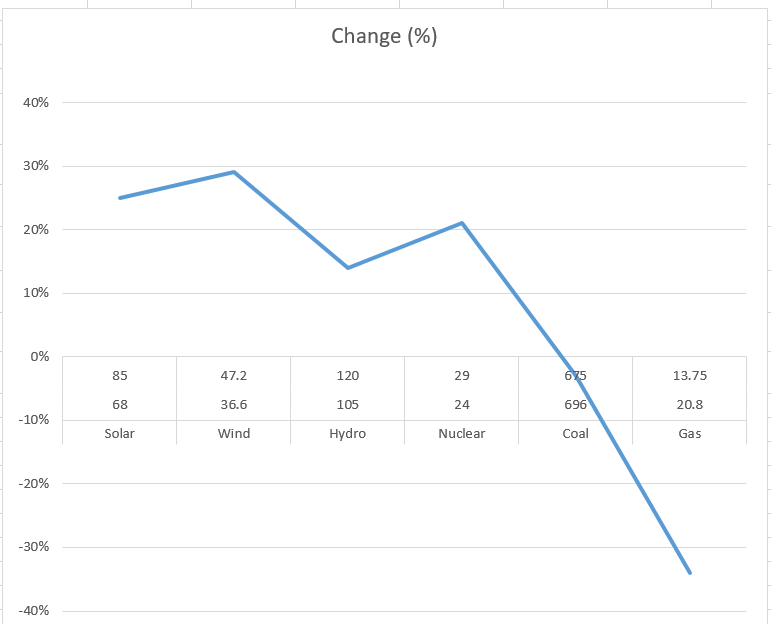
| Source | H1 2024 (TWh) | H1 2025 (TWh) | Change (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solar | 68 | 85 | +25% |
| Wind | 36.6 | 47.2 | +29% |
| Hydro | 105 | 120 | +14% |
| Nuclear | 24 | 29 | +21% |
| Coal | 696 | 675 | -3% |
| Gas | 20.8 | 13.75 | -34% |
Clean energy’s share rose from 21% in 2024 to 25% in 2025, peaking at 31% in June.
Key Drivers Behind India Cutting Fossil Electricity
Government Policies and Incentives
- Renewable energy target: 500 GW by 2030.
- Tax benefits and subsidies encourage private investment.
- Domestic manufacturing of clean energy technologies supports local economies.
Economic Pressures and Energy Security
- Reduced fossil fuel imports save billions annually.
- Domestic production reduces exposure to global price volatility.
- Minimizes dependence on imported coal and gas.
Technological Innovation
- High-efficiency solar panels and improved wind turbines.
- Energy storage systems enhance grid reliability.
- Smart grids improve renewable integration.
Challenges India Still Faces
Grid Modernization
- Smart grid infrastructure is required for intermittent sources.
- Investment in transmission and distribution is essential.
Energy Storage
- Batteries and pumped hydro storage balance supply and demand.
- Limited storage slows full renewable adoption.
Policy and Rural Access
- Rural electrification and consistent supply remain a challenge.
- Effective local governance and policy execution are crucial.
What This Shift Means for You and the World
- Cleaner air and healthier communities.
- Long-term electricity cost reduction.
- Contributes to global carbon reduction targets.
- Inspires other developing nations to adopt renewable energy.
FAQ – India Cuts Fossil Electricity
Why is it important that India cuts fossil electricity?
Reduces pollution, mitigates climate change, and improves public health.
How much fossil electricity has India cut so far?
Fossil generation declined 4% in H1 2025 while clean energy hit record levels.
What energy sources are replacing fossil fuels in India?
Mainly solar, wind, hydro, and nuclear.
Will this shift make electricity cheaper in India?
Yes, renewables are now the lowest-cost electricity source in many regions.
Can India achieve a 100% clean energy grid soon?
Projections suggest a 50% clean energy mix by 2030 if current trends continue.
Conclusion — A Future Powered by Clean Energy
India’s achievement in cutting fossil electricity while boosting clean generation is a milestone in global energy transition. Every solar panel installed, every wind turbine built, and every hydro project upgraded contributes to a healthier, greener, and more resilient India.
As citizens, businesses, and policymakers, we all play a role in supporting this transition. By embracing clean energy technologies and advocating for sustainable policies, India can meet its energy needs while protecting the planet for future generations.


